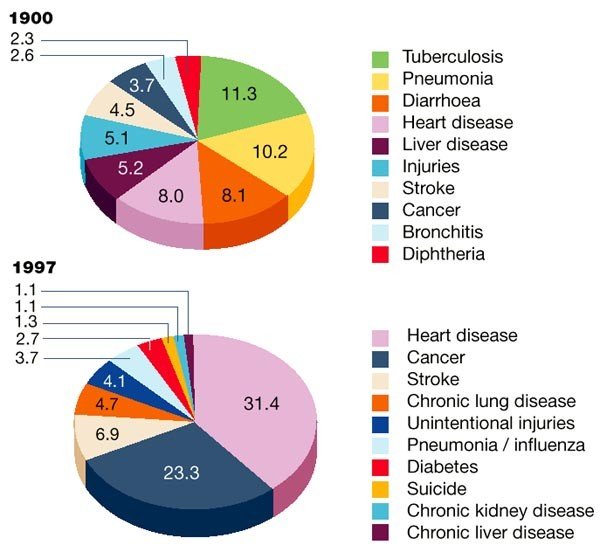
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. They are a major cause of illness and hospitalization in the U.S. CDC+1
Below, we’ll explore some of the most common infectious diseases in the United States, their symptoms, prevention methods, and potential natural support options.
Most Common Infectious Diseases in the US
According to WebMD and CDC data, some of the most frequently occurring infectious diseases in the U.S. include:
- Chlamydia WebMD+1
- Influenza (Flu A & B) WebMD+1
- Staphylococcus (Staph) infections WebMD
- E. coli / foodborne illnesses WebMD
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1 / HSV-2) WebMD
- Shigellosis WebMD
Other common ones include respiratory infections (common cold, pneumonia), urinary tract infections, and common viral illnesses. University of Utah Healthcare
Symptoms
Because each infectious disease is different, symptoms vary. However, some common signs to watch for across many infections include:
- Fever or chills
- Fatigue, weakness
- Muscle or joint aches
- Cough, sore throat, runny nose (for respiratory infections)
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
- Skin signs: rash, lesions, redness or swelling
- Pain or burning during urination (for UTIs/STIs)
If symptoms worsen, persist beyond a few days, or include warning signs like difficulty breathing, confusion, severe pain, or high fever, seek medical attention promptly.
Prevention
Preventing infectious diseases is one of the most effective ways to protect your health and others. Some key strategies:
- Vaccination: Many infectious diseases can be prevented via vaccines (e.g. flu, HPV, Hepatitis A/B).
- Hand hygiene: Wash hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating or after being in public spaces.
- Avoid touching face: Especially eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
- Safe food practices: Cook meat properly, avoid cross-contamination, wash fruits/vegetables.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Use protection (condoms) for sexually transmitted infections.
- Clean surfaces frequently, especially in shared areas.
- Healthy lifestyle: good sleep, balanced nutrition, stress management help support immunity.
Natural & Supportive Measures (Adjuncts)
While these won’t replace medical treatment, some natural or supportive measures may assist in milder cases or help your body handle infection better (always check with your doctor first):
- Probiotics: Especially helpful in GI infections to restore gut flora.
- Garlic, ginger, turmeric: Some antimicrobial and immune-supportive properties.
- Vitamin C & zinc: May modestly support immune function.
- Adequate hydration: Drink plenty of water, oral rehydration in diarrheal diseases.
- Rest & sleep: Helps your body focus energy on healing.
- Warm salt water gargle for throat infections.
- Herbal teas with soothing properties (e.g., ginger tea, chamomile)
External Reference
For detailed U.S. infection statistics and trends, see CDC FastStats – Infectious Disease which reports on cases like tuberculosis, salmonella, etc. CDC
🎥 Video Explanation
Here’s a good video that gives an introduction to infectious diseases — what they are, how they spread, and basic concepts:
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. If you suspect you have an infection or serious symptoms, always consult a qualified healthcare provider. The information here is based on current sources but may change with new research.